Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) has rapidly shifted from a niche topic to a central pillar of the global climate strategy. As governments, corporates, and investors look beyond emissions reductions, the role of large scale removals is coming into focus.
To provide clarity on where the market stands and where it is heading, AlliedOffsets has released the Carbon Removal Market Outlook (October 2025) report. Drawing on more than 60 academic studies and leading literature, the report lays out what is technically possible, what it will cost, and what level of investment will be required to meet global net zero targets.
The report can be downloaded here:
Executive Summary
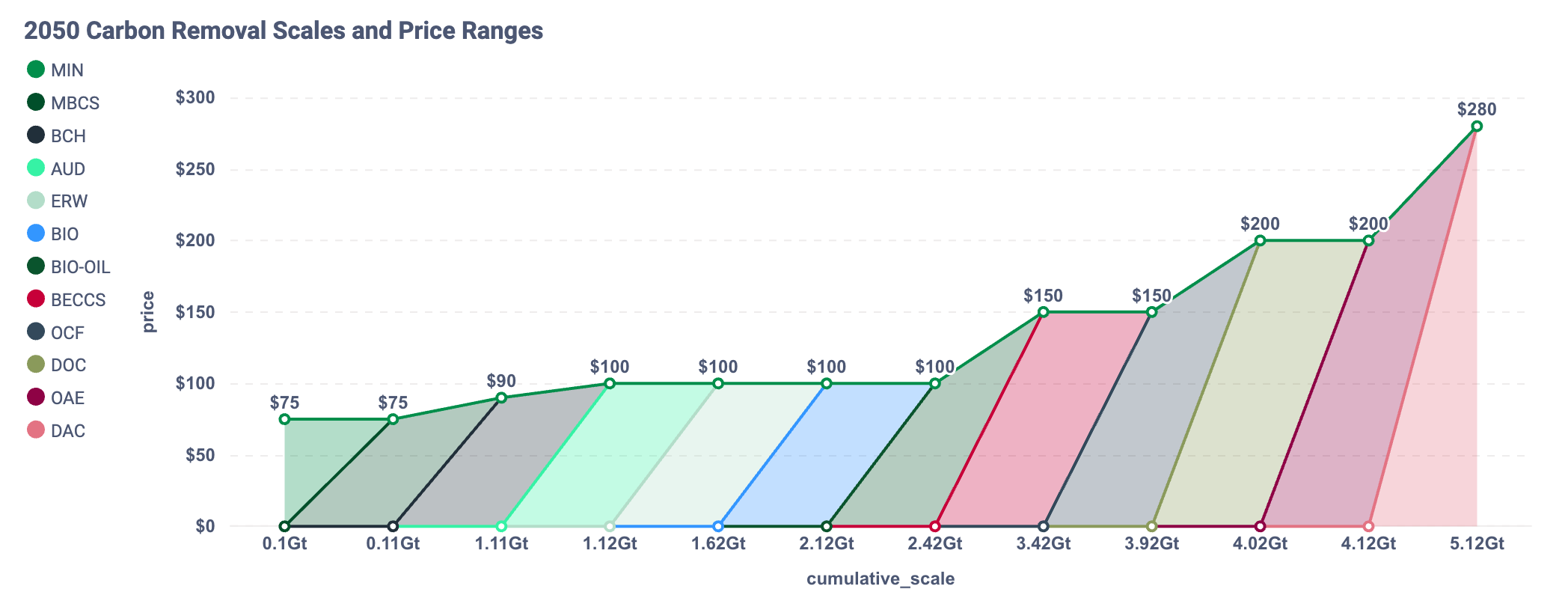
The analysis indicates that achieving global net zero by 2050 will require both deep emissions reductions and large scale deployment of carbon dioxide removal (CDR), ranging from 5 gigatons per year in the low scenario to 22 gigatons in the high scenario. Encouragingly, nearly all technical removal approaches assessed show meaningful potential at gigaton scale.
At an average cost of around $160 per ton, technological removals could effectively negate all residual emissions by 2050, provided that sharp emissions reductions happen in parallel.
 2050 Carbon Removal Scales and Price Ranges (Low Scenario)
2050 Carbon Removal Scales and Price Ranges (Low Scenario)
A cluster of scalable and cost effective solutions, biochar (BCH), bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), enhanced rock weathering (ERW), and biomass storage, could together provide nearly half of all removals. These technologies are notable not just for their climate impact, but also for their co-benefits such as soil enhancement, renewable energy generation, and support for sustainable agriculture.
Technology Outlook
Looking at the largest theoretical pathways identified in the literature:
- Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement (OAE): up to 100 GtCO2/year potential.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): upper end of -40 GtCO2/year.
- BECCS: around 11 GtCO2/year potential.
While costs today remain high for emerging approaches like DAC and OAE, both are expected to experience steep learning curves that bring prices down over time. BECCS starts from a lower baseline, with slower declines, but remains a cost competitive option long term.
Investment Needs
Scaling CDR to meet a low scenario trajectory will require $1.22 trillion in cumulative investment by 2050. In higher demand pathways, this could rise to $5.8 trillion.

Interim Revenue Required to Deliver at Scale in Low Scenario
DAC alone represents more than a third of this capital requirement, followed by BECCS and biochar. Despite their different readiness levels, these technologies are projected to be critical building blocks in the portfolio of solutions needed to deliver removals at scale.
Conclusion
The carbon removal market outlook report makes it clear that no single solution will be enough, rather a portfolio of methods will be required to help achieve net zero.
For a deeper dive into the scenarios, cost pathways, and sectoral opportunities, the report is available to download below.