Introduction
Direct Air Capture (DAC) Technology is a process that captures carbon dioxide (CO2) directly from the atmosphere.¹
It is typically coupled with utilization or storage technology.
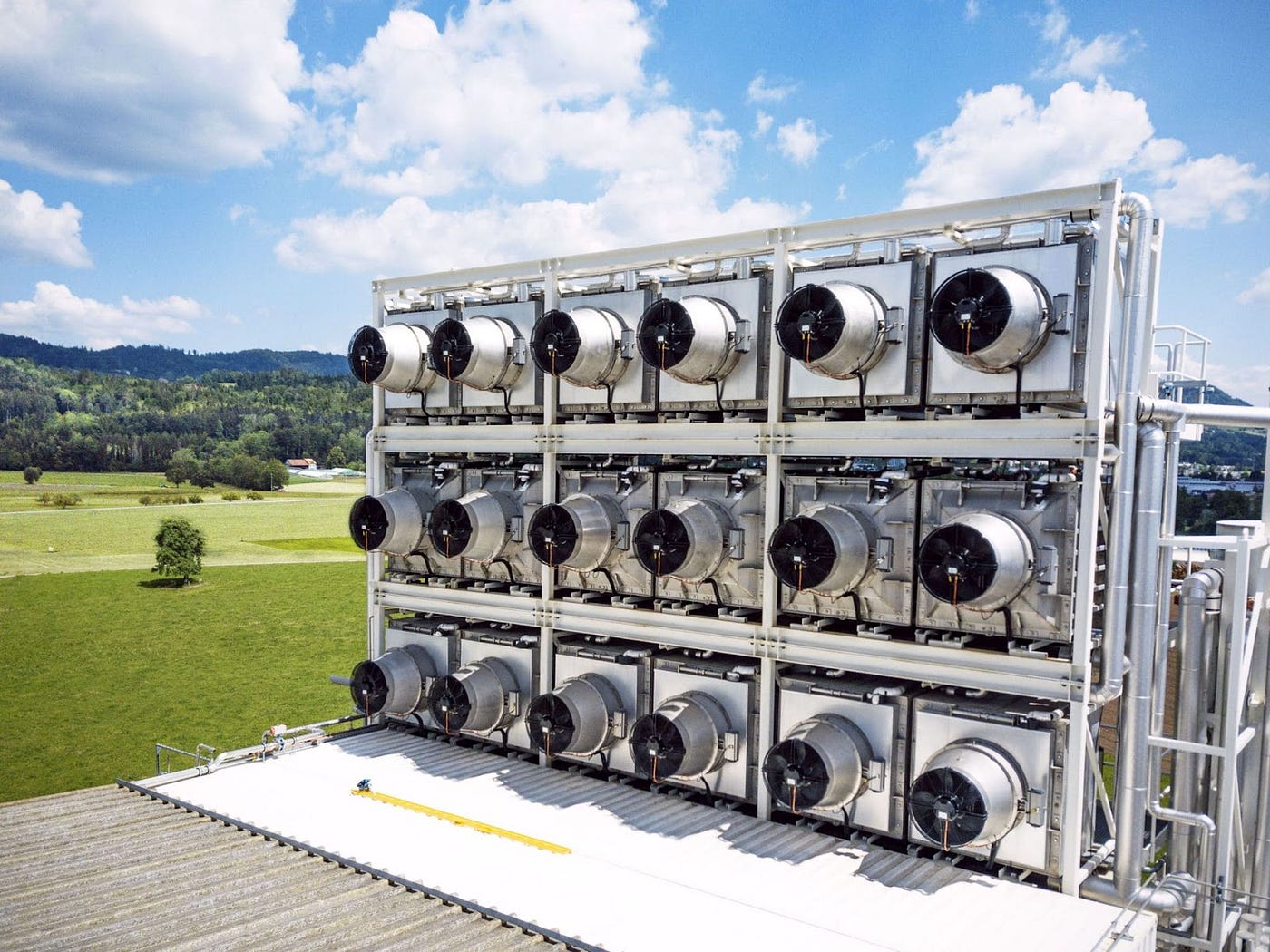
The captured CO2 is then transported to a storage site, usually deep underground, and stored in geological formations such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs, saline aquifers, or unmineable coal seams. Figure 1 shows what a typical DAC plant looks like.

The latest IPCC report has deemed that to reach a 1.5 degree target, we need to heavily supplement our carbon offsetting methods with carbon dioxide removal (CDR). DAC is one of the most promising ideas in a suite of technologies that is aiming to be scaled and distributed globally to remove carbon from our atmosphere.
At present, there are 19 DAC plants in operation worldwide, which capture approximately 0.01 Mt CO2 per year annually, are still in their infancy and are expensive². However, there is a plant that is aiming in capturing 5 Mt CO2 per year and is currently in advanced development in the United States, Project Bison. The way this DAC plant works is that it has individual DAC machines in modules that it can just stack on top of each other in a large grid. The timeline is to take in 10,000, 200,000, 1MT and 5MT of CO2 per year by 2024, 2026, 2028 and 2030 respectively.⁴
In order to achieve the goal of net zero emissions by 2050, it is projected that DAC will need to be scaled up significantly, to capture nearly 60MtCO2 per year by 2030. While this level of deployment is feasible, it will require the construction of several more large-scale demonstration plants to refine the technology and reduce the costs associated with capturing CO2 from the air.
This blog is going to outline how this technology works and the space it takes up in the VCM.
DAC Technology
DAC technology works by pulling CO2 from the ambient air using a combination of chemical processes and mechanical filters.
Currently there are two main technological approaches are currently being used to capture CO2 from the air:
Solid DAC (S-DAC)
- Solid adsorbents operating at ambient to low pressure under a vacuum and medium temperature of 80–120 degrees. Companies that work on S-DAC systems: Climeworks⁵, Global Thermostat⁶, Infinitree⁷ and Skytree⁸.
Liquid DAC (L-DAC)
- Liquid DAC relies on an aqueous basic solution (such as potassium hydroxide), which absorbs carbon and releases the captured CO2 through a series of units operating at high temperature (between 300 degrees and 900 degrees )⁹. Companies that work on L-DAC: Carbon Engineering¹⁰, Climeworks, Global Thermostat.
The main distinction between the two types of DAC is the separation mechanism, what materials and physical mechanisms do we use to separate CO2 from the air and store it.
Terminology
To explain DAC in full, there are some physical concepts that are surrounding the process of separation of CO2 from the air that need to be clarified first: adsorption, solvent, regeneration, and contactor.
Adsorption: Adsorption is a process in which molecules or particles from a substance (“adsorbate”) adhere to the surface of another substance (“adsorbent”). This adhesion is typically caused by attractive forces between the two substances. Adsorption is not to be confused with absorption which is where molecules percolate inside the material instead of attaching themselves to the surface. The distinction between the two can be seen in figure 2.
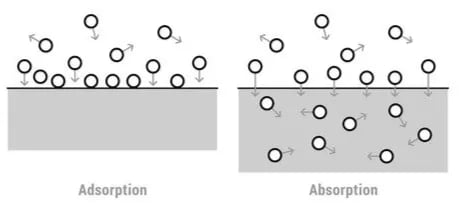
This is the main process of separation feature of S-DAC. Where CO2 is adsorbed to the surface of a sorbent typically a zeolite. Sorbents are materials that are capable of adsorbing other substances, in other words, a substance that can attract and hold onto other molecules or particles on its surface.
Solvents: A solvent is a substance that can dissolve other substances, which are called solutes. When you add a solute to a solvent and stir or mix them together, the solute particles break apart and mix evenly throughout the solvent. This creates a homogeneous mixture called a solution. A visual representation of this can be seen in figure 3.

This is the main separating mechanism of L-DAC. L-DAC has a very specific liquid solvent system which is designed to selectively extract the solute CO2 out of the air, this is typically potassium hydroxide which is put into a chemical system which can be found here: L-DAC Solvent Explanation.
Regeneration: is the concept for both L-DAC and S-DAC that occurs when the separating mechanism, the sorbent or solvent are saturated, meaning that the capacity of CO2 that those materials has is full and the mechanism needs to release and store that CO2 and regenerate the sorbent or solvent. This normally occurs under high pressure and temperature and is one of the most energy intensive processes in DAC.
Contactor: In the context of L-DAC, a contactor is a device or vessel that facilitates contact between the liquid solvent used to capture carbon dioxide and the air drawn into the L-DAC unit. The contactor is designed to maximize the surface area of the liquid solvent and to allow for efficient and effective capture of carbon dioxide molecules from the air.
DAC, Step by Step
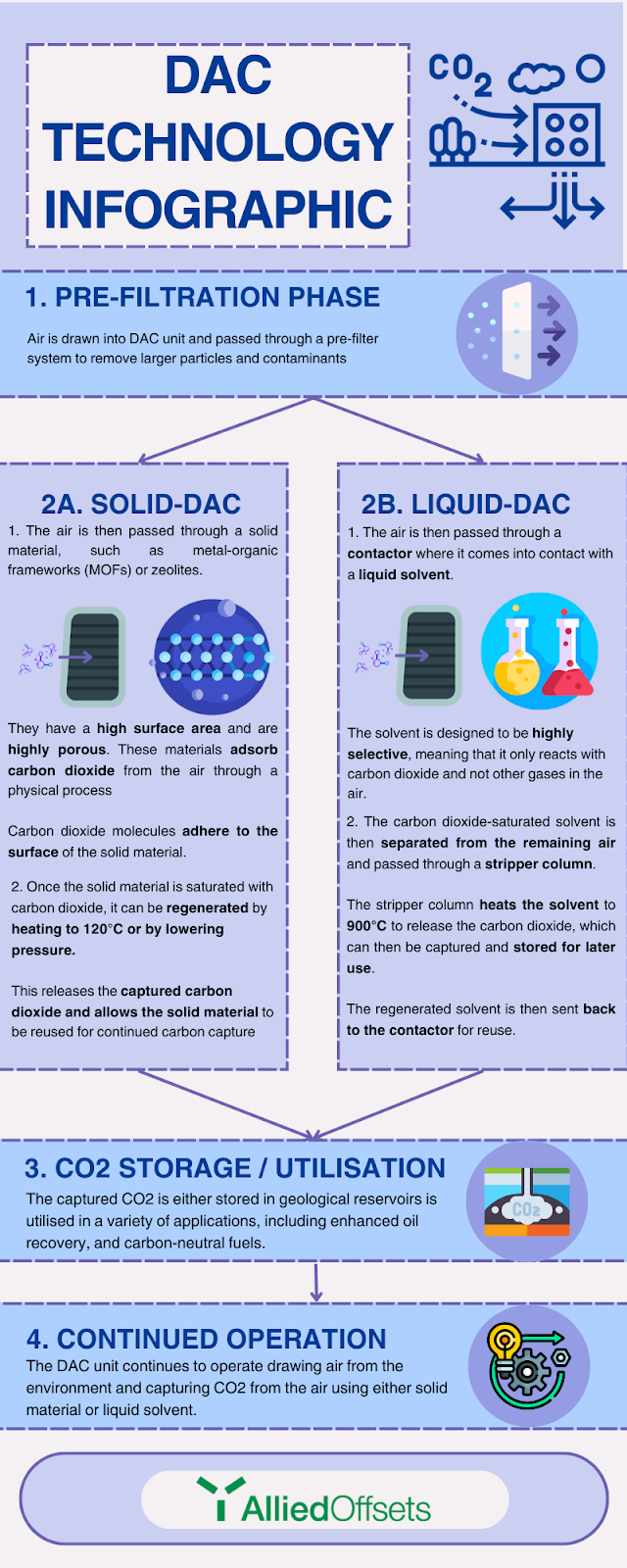
Typically there are four main steps in how a DAC plant operates. At a high level are:
- The Pre-filtration Phase
- Separation Phase — This is the main distinction between using S-DAC or L-DAC methods
- CO2 Storage / Utilisation
- Continued Operation
Figure 4 is an infographic that provides information on each of these phases:
If you want to explore a deeper look at the inner workings of DAC, some accessible videos on L-DAC and S-DAC are available below. They are based on a textbook written about DAC by the National Academy of Sciences:
- L-DAC Scientific Mechanism Overview
- S-DAC Scientific Mechanism Overview
- DAC Methods Scientific: National Academy of Sciences
Current State of DAC Technology
Currently the price of DAC per tCO2e is about 2–6 times higher than the desired price and depends highly on the energy used.
DAC technologies still need to improve in three areas: sorbent / solvent, regeneration, and contactor to drive down costs.
Technology — based economic development in all three areas are required to achieve <$100/ton of CO2 which makes DAC economically viable.¹¹
S-DAC & L-DAC innovation efforts are mostly focussed on innovation sorbents and solvents, and optimised processes and layouts, however there are emerging DAC technologies (Technological readiness level 6) which include electro-swing adsorption (ESA)¹² and membrane-based DAC (m-DAC).¹³
- ESA is based on an electrochemical cell where a solid electrode adsorbs CO2, when negatively charged and releases it when a positive charge is applied (swinging the electric charge, rather than the operating temperature or pressure as happens in other physical separation techniques).
- m-DAC has been proposed as another feasible option for capturing CO2 from the air; however, it is still in its infancy and major challenges are yet to be overcome (including the need for the expensive compression of a very large amount of ambient air to separate CO2 efficiently).
- Another kind of DAC which is passive and does not require any dynamic parts and has no thermal energy requirements. Passive DAC — Mechanical Tree is designed by the researchers at Arizona State University.¹⁴
Comparison with other carbon capture technologies
BeZero filed a CDR scalability report¹⁵ that compares the most promising suite of CDR technologies to each other in eight dimensions of scalability; find out more here. DAC has some of the highest policy and regulatory assistance particularly in the US with high funding assistance from policy sources. However, the absolute capital the technology needs relative to other technologies is the largest overall. DAC also requires one of the largest amounts of resources to be built, especially concrete, steel, plastics and water, due to facility storage and requirements. DAC particularly has a large reliance on sorbent supply chains.
One of the main advantages of DAC technology is that it can capture CO2 emissions from any source, regardless of the type of industry or equipment that is emitting the CO2 and fairly low requirements for MRV to be put into place compared to CDR technologies such as Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement.
DAC in the VCM
There are currently 78 unregistered DAC projects situated in 19 different countries in our database at AlliedOffsets. 47% of DAC projects are located in the USA, 14% in Canada and 11% in the UK. The average price of DAC credit is $886, this is 443% higher than the expected price the American University has expected DAC to be at scale.¹⁶ The largest buyers are Square, Microsoft, Priva Capital and Klarna. DAC is estimated to sequester 60MT/CO2 per year by 2030.¹⁷ Today it is at 0.01 MT/co2 per year.
Challenges and limitations of DAC technology
The major challenge and limitation for DAC is the cost of each of these plants. While there is a large construction cost, the energy usage of DAC is extremely high with L-DAC and S-DAC using approximately 6.5GJ and 10GJ per tonne of CO2 respectively.¹⁸ This energy cost is mainly due to the regeneration of solvents and sorbents, which requires the heating of those materials to 120–900 degrees for a few minutes. To put the idea of GJ in perspective to its fuel source to produce 1 GJ/s you would have to have 3 million photovoltaic cells hooked up to the DAC plant¹⁹, and therefore this cost needs to drop substantially with research into solvent, contactor and regeneration technology.
Innovation is also needed across the DAC value chain. While S-DAC could be powered by a variety of low-carbon energy sources (e.g. heat pumps, geothermal, solar thermal and biomass-based fuels), the current high-temperature needs of today’s L-DAC configuration does not allow that level of flexibility and could at best operate using low-carbon fuels, such as biomethane or renewables-based electrolytic hydrogen. In the future, L-DAC could shift to fully electric operation and large scale L-DAC plants will be designed to use natural gas for heat to co-capture the CO2 produced during combustion of the gas without the need for additional capture equipment.
This would be beneficial because it would help to reduce the overall cost of carbon capture as it will allow L-DAC plants to generate revenue from the sale of captured CO2. Natural gas is relatively cheap and abundant source of fuel, and using it to heat the L-DAC plant could be more cost-effective than using other energy sources, such as solar power. In addition capturing CO2 emissions from natural gas combustion could help reduce the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas production and use. By co-capturing the CO2 produced during combustion, L-DAC plants could help to offset some of the emissions associated with natural gas use, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Depending on whether the electricity grid becomes increasingly powered by renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, it may become possible to power L-DAC plants entirely by electricity, eliminating the need for fossil fuels altogether.
Conclusion
Advanced CDR technologies need to be developed to supplement avoidance and reduction mechanisms for CO2. As stated by the latest IPCC report, we cannot reach 1.5 degrees without CDR.
DAC is one of the most promising CDR technologies that is being researched. Currently at technology readiness level 6 and an average credit price at $886 per tCO2, DAC still has a long way to go, but it does have high policy and regulatory support.
Technologically there are two main types of DAC, solid sorbent S-DAC and liquid solvent L-DAC. The difference between them are the physical CO2 capture mechanisms. More research is needed in the sorbent, regeneration and contactor technology to scale DAC, which at the moment cause there to be high energy costs which need to be overcome to reach the 30MT/CO2 per year projections for DAC by 2030.
